Agentic AI represents the next leap forward in artificial intelligence, moving beyond simple prompt-response systems. Most AI tools are limited to generating text, images, or predictions when asked. In contrast, agentic AI actively understands its environment, sets goals, and takes action to achieve them.
A recent Gartner report highlighted that fewer than 1% of enterprise software applications made use of agentic AI in 2024. That figure is expected to rise sharply to 33% by 2028. This growth shows how businesses recognize the immense value of agentic AI — and by the end of this article, you’ll see why too.
What Is Agentic AI?
Understanding the Impact of Agentic AI
At present, there isn’t a single, universally accepted definition of agentic AI. Some experts use “agentic AI” and “AI agents” as synonyms, while others differentiate between them. However, most agree that it is about autonomous systems that can plan, decide, and act toward goals.
Unlike traditional AI, which produces results only when prompted, agentic AI can:
- Analyze situations in real time.
- Develop strategies and workflows.
- Execute actions without constant guidance.
- Decide how to use tools and adapt internal processes.
Think of it like an autonomous vehicle. It doesn’t just move when told — it constantly evaluates road conditions, adjusts routes for efficiency, responds to traffic signals, and ensures it reaches its destination. That’s autonomy, adaptability, and goal-driven behavior in action.
Agentic AI vs. Traditional AI
Autonomy and adaptability are the primary distinctions between agentic AI and classical AI.
- Traditional AI is taught with a specific goal in mind. Although it generates output and processes data, it is unable to make decisions on its own. Examples include chatbots and recommendation algorithms.
- By actively planning, adapting, and making decisions, Agentic AI goes beyond this. It can communicate with many systems, hone its goals, and complete tasks in advance.
| Feature | Traditional AI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Only responds to input | Can act independently and adapt |
| Decision-Making | Follows predefined rules | Refines objectives and strategies in real time |
| Interaction | Limited to input-output cycles | Works with multiple tools, APIs, and systems |
| Learning | Needs retraining to improve | Learns dynamically and optimizes workflows |
| Flexibility | Narrow use cases | Handles multi-step, complex processes |
| Use Cases | Predictions, automation | Autonomous research, task execution |
| Limitations | Rigid, task-bound | Requires oversight and has higher risks |
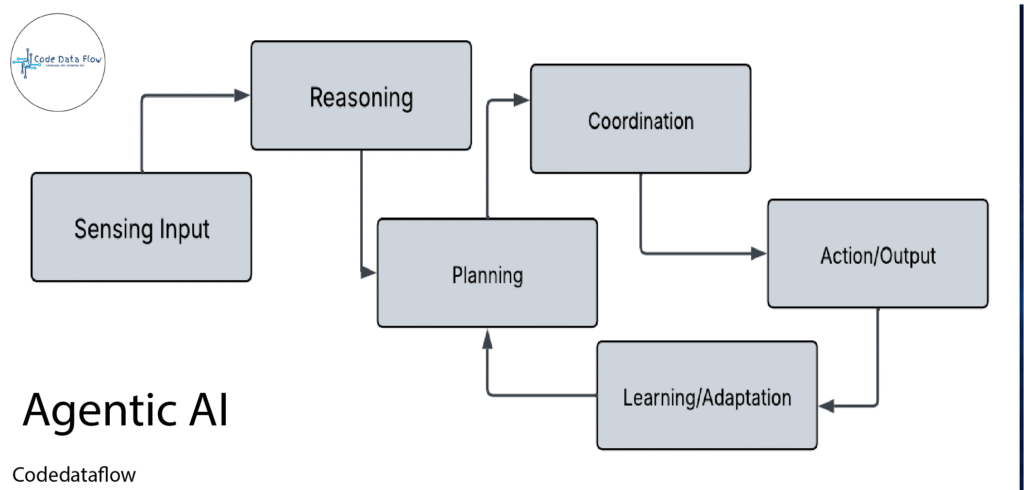
How Does Agentic AI Work?
Agentic AI isn’t a single tool or technology — it’s an approach to building AI systems with independence baked in. Most setups involve:
- Multiple Models with Different Roles:
Agentic AI systems frequently employ several models cooperating rather than a single huge model controlling everything. For example, a “manager” model may break down an objective into smaller tasks, allocate those to specialized sub-models, and then aggregate the outputs. The system can manage more complicated operations because to its modular architecture.
- External Tools and Data Access:
Agentic AI relies on more than language models alone. It makes connections to databases, software tools, and APIs in order to process files, obtain data from the real world, and communicate with apps. Frameworks like LangChain and LlamaIndex assist bridge LLMs with other technologies.
- Asynchronous, Distributed Processing:
The Role of Agentic AI in Modern Technology
These systems frequently operate asynchronously, in contrast to classical AI, which completes tasks one at a time. The system can operate more quickly and efficiently when several activities are carried out concurrently. A research assistant, for example, may have three models working simultaneously: one collecting materials, one analyzing them, and a third synthesizing a summary.
Applications of Agentic AI
Agentic AI has potential across industries. Some notable applications include:
- Healthcare: Monitoring patient data, detecting anomalies, and recommending treatment options — easing the workload for doctors and improving efficiency.
- Gaming: NPCs (non-player characters) that adapt to player behaviour, pursue goals, and evolve dynamically, creating richer gameplay experiences.
- Finance: Real-time trading systems that analyze market conditions, execute trades, and adjust strategies without human intervention.
- Research & Knowledge Work: Assisting with literature reviews, synthesizing reports, and even running experiments autonomously.
key Benefits of Agentic AI
This technology holds potential for relieving humans of low-level, repetitive activities so they can concentrate on strategic and creative work. It has the ability to spur innovation in the same way that calculators freed us from laborious math and computers mechanized data entry.
Exploring the key Benefits of Agentic AI
- Faster experimentation: Professionals can test more ideas in less time.
- Democratized expertise: Smaller teams gain access to decision-making power once limited to large organizations with specialized experts.
- Efficiency and productivity: Workflows can be streamlined across industries, from healthcare to business operations.
Challenges and Risks of Agentic AI
Despite its potential, agentic AI raises important challenges:
- Ethics and Governance: Without regulations, autonomous AI actions could cause unintended harm. Clear rules are needed before agentic AI takes on high-stakes decisions.
- Socio-Economic Impact: Automation may displace certain jobs, creating a need for reskilling and workforce adaptation.
- Transparency: As systems become more complex, understanding their decision-making processes becomes harder — increasing accountability concerns.
The Future of Agentic AI
Looking ahead, agentic AI will likely evolve toward greater autonomy, personalization, and accessibility.
- Self-Improving Systems: AI that not only executes goals but refines its own methods and objectives.
- Low-Code/No-Code Development: User-friendly platforms will let non-technical people create custom AI agents for personal or business needs.
- Personalized AI Partners: Instead of generic assistants, AI systems will adapt to individuals — learning their preferences, workflows, and styles over time.
Conclusion: Why Agentic AI Matters
Agentic AI represents a turning point in artificial intelligence: from reactive systems that wait for instructions to autonomous agents that plan, decide, and act. While challenges around ethics, safety, and transparency remain, the potential benefits for innovation, productivity, and accessibility are enormous.
The emergence of agentic AI points to a day when it will not only be a tool but also a digital partner that helps us accomplish our objectives. One thing is certain: the era of agentic AI will change the way people and machines interact, even though the trip is only getting started.