Loops in Python – Complete Guide with Examples
In this lecture we will cover : Loops in Python: Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to For, While, Break, Continue & range()
Loops are a fundamental concept in programming that allow us to execute a block of code multiple times. In Python, loops help reduce redundancy, make code concise, and improve readability.
This lecture covers:
- What are Loops?
whileLoopsforLoops andrange()breakStatementcontinueStatement- Nested Loops
What are Loops in Python?
Definition:
A loop is a programming construct that iterates through a block of code as long as a particular condition is true.
Python includes two primary categories of loops that are most commonly employed:
whileloop
forloop
While Loops in Python
Definition:
A while loop keeps executing the block of code as long as the condition is true.
Syntax:
while condition:
# code block
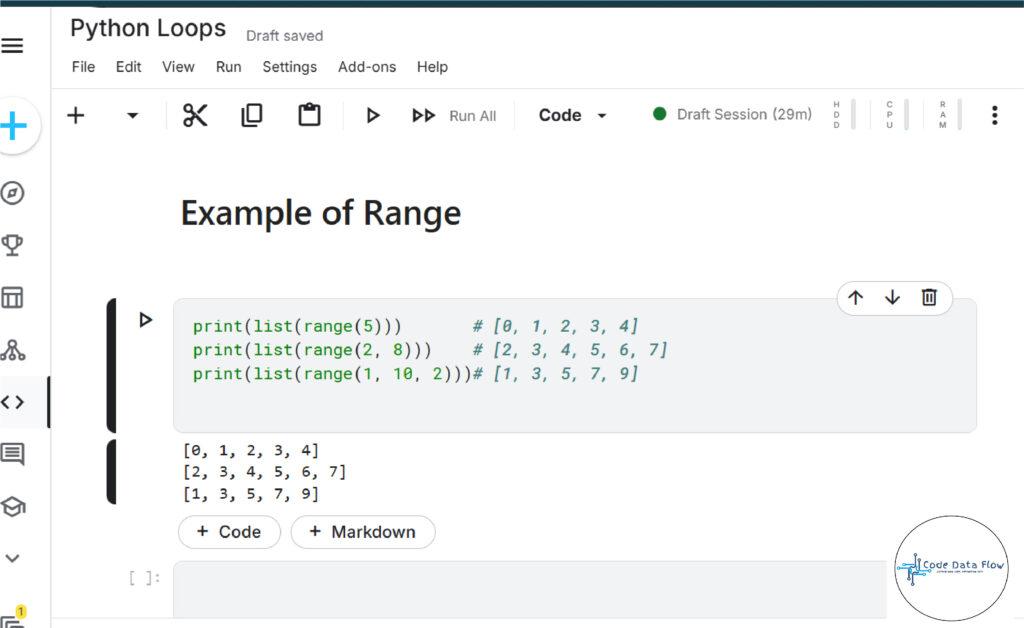
range() in Python:
Definition:
The function range() creates a sequence of numbers to be used for for loops most of the time.
Syntax:
range(start, stop, step)
start(optional) – starting number (default is 0)
stop– generates up to this number (not inclusive)
step(optional) – difference between each number (default is 1)
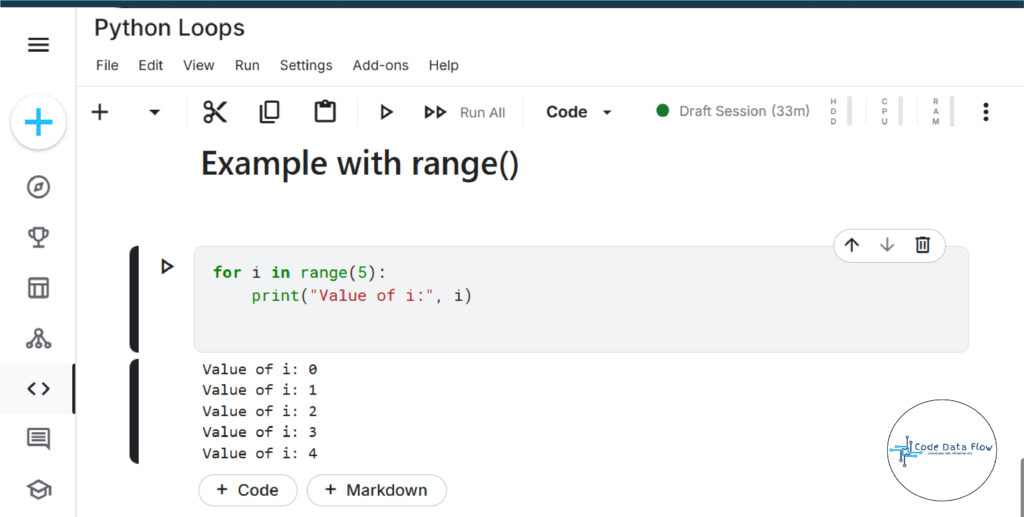
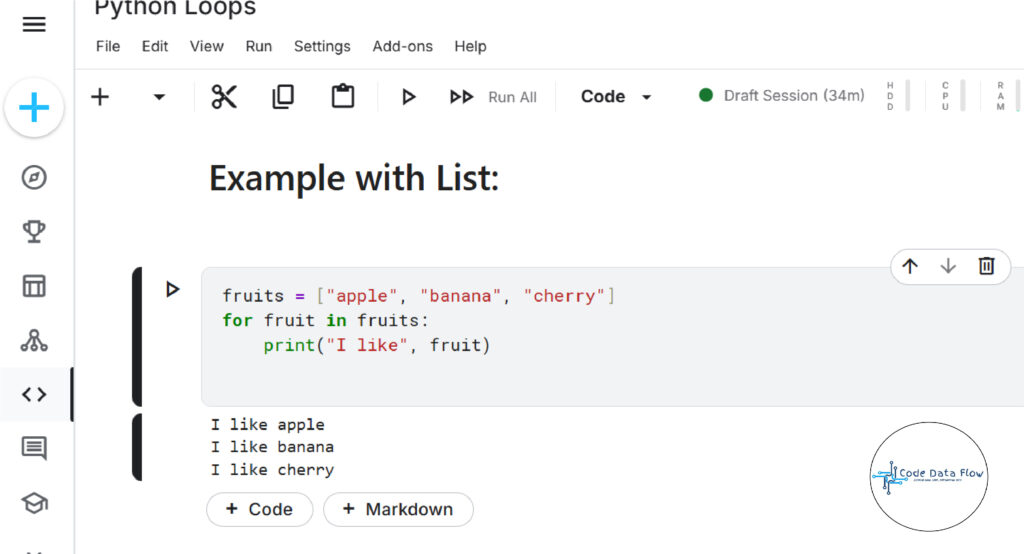
For Loops in Python
Definition:
A for loop is utilized for traversing the elements of some arrays such as lists, tuples, or ranges.
Syntax:
for item in sequence:
# code block
Break in Python
Definition:
The break statement is utilized for leaving the loop prematurely, regardless of whether the loop condition is still true.

Continue in Python
Definition:
The continue statement helps to skip the current iteration and reach the next one.

Nested Loops in Python
Definition:
A nested loop is a loop that is defined inside another loop. Whenever the outer loop is executed, the inner loop is executed in full.

Summary Table
| Concept | Use | Example |
|---|---|---|
while loop | Loop until a condition is false | while count < 5: |
for loop | Loop over sequences or ranges | for i in range(5): |
range() | Generate sequence of numbers | range(1, 10, 2) |
break | Exit loop early | if x == 5: break |
continue | Skip current iteration | if x == 3: continue |
| Nested loops | Loop inside a loop | for x in range(3): for y in ... |
🧠 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Loops in Python
❓ What is the difference between for and while loops in Python?
The main difference lies in how they repeat:
for loop is used when you know how many times you want to run a block of code. It’s often used with functions like range(), lists, or strings.
for i in range(5):
print(i)
while loop is used when you want to repeat until a condition is no longer true, and you might not know in advance how many times it will run.
i = 0
while i < 5:
print(i)
i += 1❓ When should I use break in a Python loop?
Use break when you want to exit the loop early, before the loop naturally finishes all iterations.
Example:
for num in range(10):
if num == 5:
break
print(num)
This loop stops printing when num reaches 5.
❓ What does continue do in Python loops?
The continue statement skips the current iteration and moves to the next one.
Example:
for num in range(5):
if num == 2:
continue
print(num)
Output: 0 1 3 4 — Notice how 2 was skipped.
❓ Can loops be nested in Python?
Yes! You can write a loop inside another loop, which is called a nested loop. It’s useful for working with 2D data structures like matrices or grids.
Example:
for i in range(3):
for j in range(2):
print(f"i={i}, j={j}")
❓ What is the use of range() in Python loops?
The range() function is commonly used with for loops to generate a sequence of numbers.
Example:
for i in range(1, 6):
print(i)